Sensitivities Panels
One of the most important parts of any nodal analysis is quantifying how much the results change when you vary a single parameter. First identify which parameters actually move the needle, then spend time improving those inputs.
SNAP builds the Sensitivities panels from parameters already present in the dataset. It separates them into two tabs based on whether they impact the IPR curves or the hydraulics curves, and in rare cases both.
Why run sensitivities first?
Sensitivities help you focus effort on the inputs that matter most. Tune those first, and avoid overworking low-impact parameters.
The plot below shows a water cut sensitivity, which is one of the few cases that affects both the Hydraulics and IPR curves.
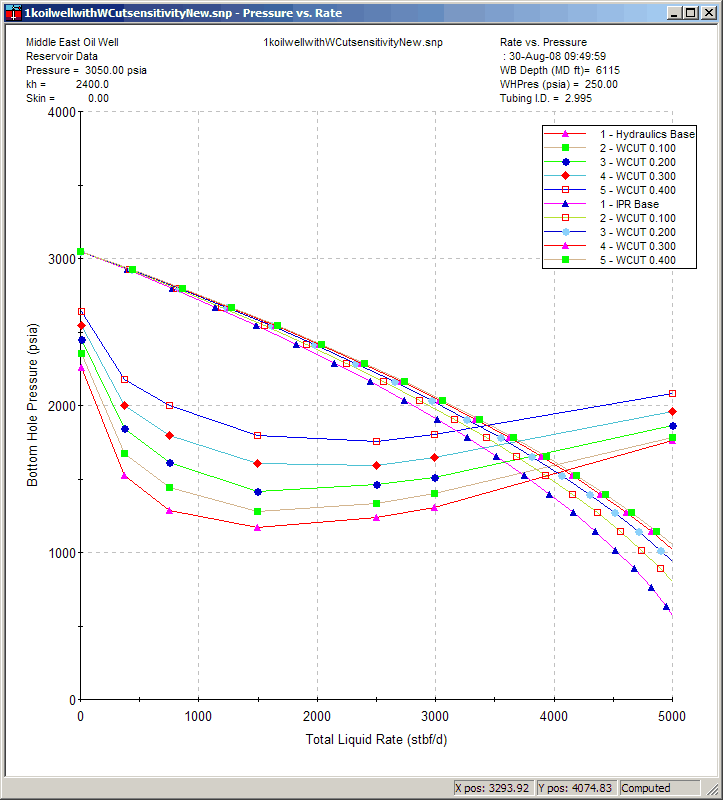
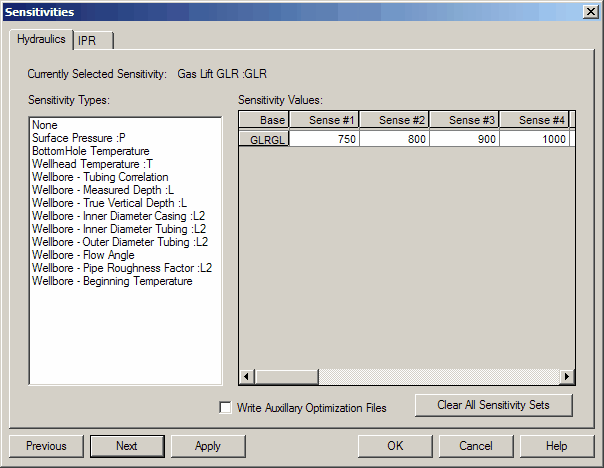
1. Hydraulics Sensitivities
This dialog lets you pick which hydraulic parameters to vary and see how changes affect the system.
Context-aware list
Parameters that do not apply to the current case are hidden. For example, flowline I.D. is not shown if no flowline exists.
1.1 Tubing and Flowline Sensitivities
- Separator pressure (psi): Pressure at the end of the flowline. Not available when no flowline exists.
- Wellhead pressure (psi): Surface flowing pressure at the wellhead. Not valid when a flowline exists since the wellhead becomes an internal node.
- Flowline I.D. (in): Internal diameter from separator to wellhead. If multiple segments exist, enter all segment sizes. Not available when no flowline exists.
- Tubing I.D. (in): Internal diameter from wellhead to bottomhole. If multiple segments exist, enter all segment sizes. Not available when flow is through the annulus.
- Tubing O.D. (in): Outer diameter for annular-flow cases. If multiple segments exist, enter all segment sizes. Not applicable when flow is inside the tubing.
- Gas–liquid ratio (scf/bbl): Gas divided by (oil + water) for simple gas-lift entry. Should not be less than solution GOR. Available only for gas-lift wells.
- Injected gas rate (mscfd): Lift-gas injection rate. Available only for gas-lift wells.
- Tubing correlation: Choose among multiphase vertical correlations to compare differences.
- Flowline correlation: Choose among horizontal correlations to compare differences. Not available when no flowline exists.
1.2 Other Hydraulic Sensitivities
- Mona coefficient A1
- Mona coefficient A2
- Gas-lift GLR
- Measured depth of injection
- Gas-lift pressure
- Surface pressure
- Gas-lift rate
- Specific gravity of gas-lift gas
- Bottomhole temperature
- Gas-lift temperature
- Surface temperature
- Wellhead temperature
- Wellbore: Tubing correlation
- Flowline: Measured depth
- Flowline: True vertical depth
- Flowline: Inner diameter casing
- Flowline: Inner diameter tubing
- Flowline: Outer diameter tubing
- Flowline: Flow angle
- Flowline: Pipe roughness factor
- Flowline: Beginning temperature
- Flowline: Measured depth of a restriction
- Flowline: Restriction diameter
- Flowline: Tubing correlation
- Wellbore: Measured depth
- Wellbore: True vertical depth
- Wellbore: Inner diameter casing
- Wellbore: Inner diameter tubing
- Wellbore: Outer diameter tubing
- Wellbore: Flow angle
- Wellbore: Pipe roughness factor
- Wellbore: Beginning temperature
- Wellbore: Measured depth of a restriction
- Wellbore: Restriction diameter
1.3 Combined Sensitivities
- Water cut (fraction): Affects both IPR and tubing hydraulics, so it runs as a combined sensitivity. Selecting this turns off all other sensitivities.
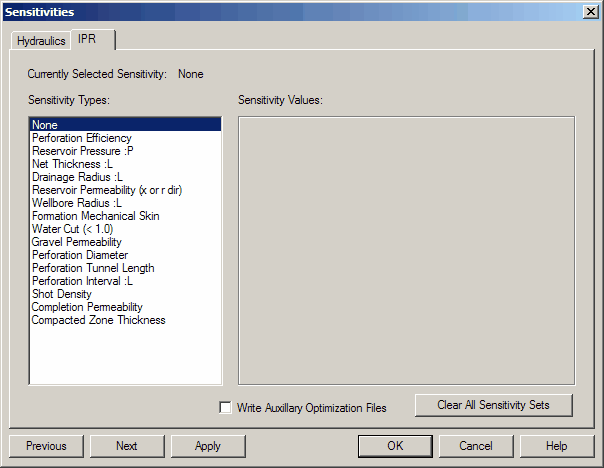
2. IPR Sensitivities
This dialog lets you pick IPR parameters to vary and see how changes affect the inflow curve.
Context-aware list
Items that do not apply to the current case are hidden. For example, gravel-pack parameters are hidden when no gravel pack is defined.
2.1 Reservoir and Completion Sensitivities
- Reservoir pressure (psia): Pressure used for all defined zones. Best for depletion studies. Use with care when fixed flow rates are defined, since the IPR will try to honor all data.
- Permeability: Permeability of the first layer or the layer of interest.
- Perforation density (SPF): Net perforation density from the completion dialog. Unavailable when no completion is defined.
- Perforation diameter (in): Perforation tunnel diameter. Most important for gravel-pack completions. Unavailable when no completion is defined.
- Perforation penetration (in): Tunnel length for cased-hole completions. Unavailable when a gravel pack is defined and Flow length is used instead.
- Flow length (in): Gravel-pack flow length. Valid only for gravel-pack completions.
- Water cut: The only sensitivity that affects both IPR and multiphase hydraulics. If selected, it defines both IPR and hydraulic sensitivities. Not valid if test data is supplied, if the well is dry gas, or if another multiphase sensitivity is already selected.
- Skin: Skin factor used by the IPR. Useful for estimating stimulation impact.
2.2 Other IPR Sensitivities
- Back pressure C factor
- Perforation efficiency
- Fluid level 1
- Fluid level 2
- Back pressure N factor
- Productivity index
- Bottomhole test pressure 2
- Stabilized pressure
- Ramey D factor
- Flow rate 1
- Flow rate 2
- Test rate 1
- Test rate 2
- Stabilized rate
- Skin factor
- Constant PI reservoir pressure
- Reservoir pressure
- Net thickness
- Drainage radius
- Reservoir permeability
- Wellbore radius
- Formation mechanical skin
- Zonal water cut
- Permeability along horizontal-well axis
- Permeability perpendicular to horizontal-well axis
- Horizontal well drainage area
- Distance from heel end of drainage to heel
- Distance from heel end of drainage to toe
- Length of side along horizontal-well axis
- Distance in from side to horizontal-well axis
- Length of side perpendicular to horizontal-well axis
- Distance from top of horizontal-well area
- Fracture length
- Porosity
- Producing time
- Total compressibility
- Fracture width
- Fracture conductivity
- Gravel permeability
- Perforation diameter
- Perforation tunnel length
- Perforation interval
- Shot density
- Completion permeability
- Completion thickness
- Test rate 1
- Bottomhole test pressure 1
- Test rate 2
- Bottomhole test pressure 2
- Shut-in pressure
2.3 PVT Sensitivities
- API gravity
- FVF correlation
- GOR correlation
- Oil viscosity correlation
- Kuparuk depth
- Oil formation volume factor
- Gas–oil ratio
- Solution GOR correlation
- Liquid yield
- Bubble point pressure
- V&B reference pressure
- Gas specific gravity
- Specific gravity of free gas
- Specific gravity of solution gas
- Oil specific gravity
- Water specific gravity
- Surface tension
- V&B reference temperature
- Gas viscosity
- Liquid viscosity
- Water cut
- z-factor
- Kuparuk zone option
2.4 Combined Sensitivities
- Water cut (fraction): Affects both IPR and tubing hydraulics, so it runs as a combined sensitivity. Selecting this turns off all other sensitivities.